What is cost and the importance of cost in manufacturing?
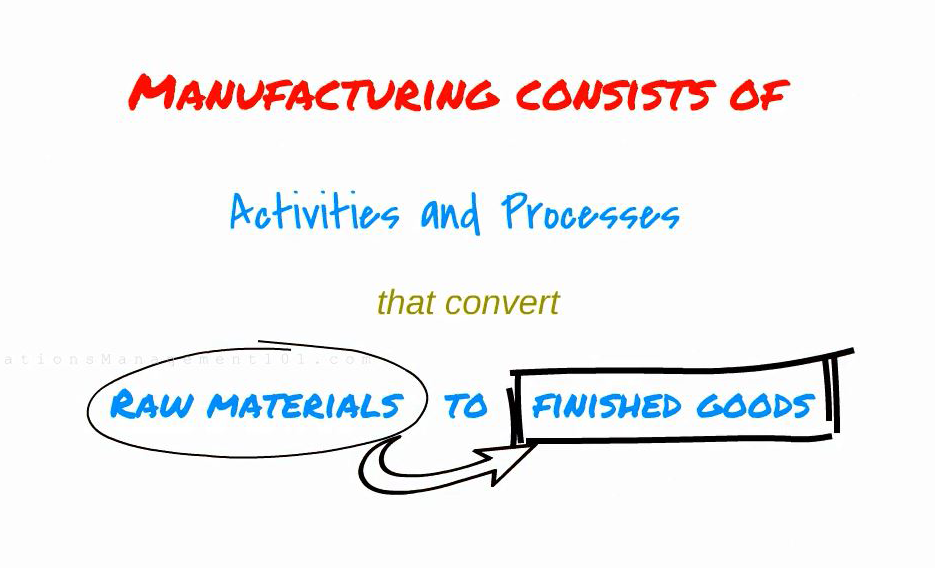
Before talking about different types of costs in manufacturing, we can quickly see what is manufacturing and what is cost. Manufacturing consists of activities and processes that convert raw materials to finished goods.
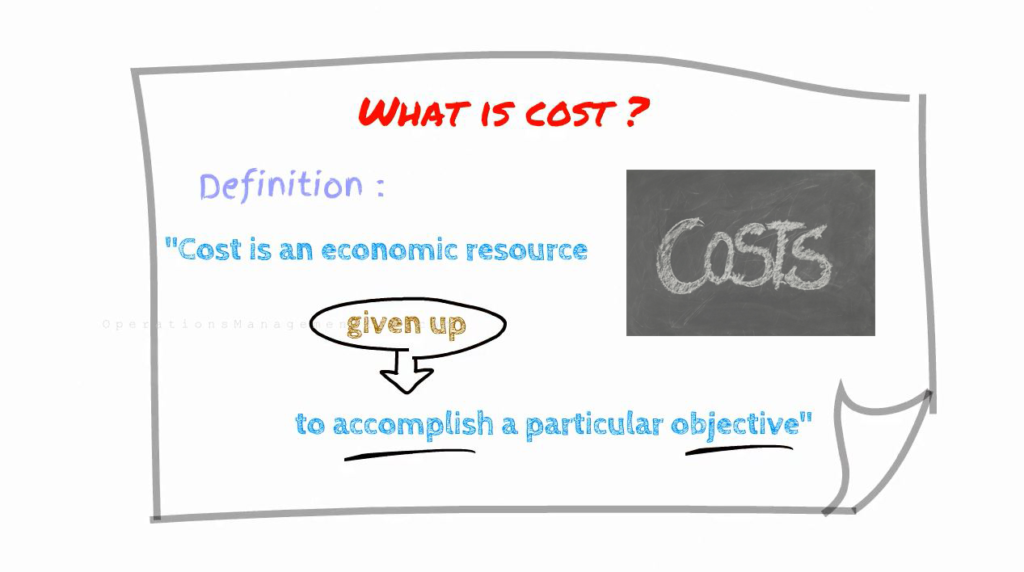
Cost is defined as “An economic resource given up to accomplish a particular objective”.
So, we can understand that different types of costs are involved in these activities and processes.
To perform management functions effectively, managers in manufacturing have to make lot of decisions.
Managers have to consider:
- What costs are involved in making a product or delivering a service?
- How to control costs? Less costs will result in more profits.
- How cost is related to production volume? Do costs decrease or increase when more quantity is produced?
This decision making needs lot of information. Cost is a very important information among these.
The following video gives you an understanding of different types of costs in manufacturing.
To know about different types of costs in manufacturing, we should know about different components and activities involved in manufacturing.
As mentioned in the beginning, manufacturing converts raw materials to finished goods. So, raw materials and conversion process are the two basic components in manufacturing.
When we go further we can understand that:
- Raw materials consists of Direct Materials and Indirect Materials.
- Conversion process consists of Direct Labour and Indirect Labour.
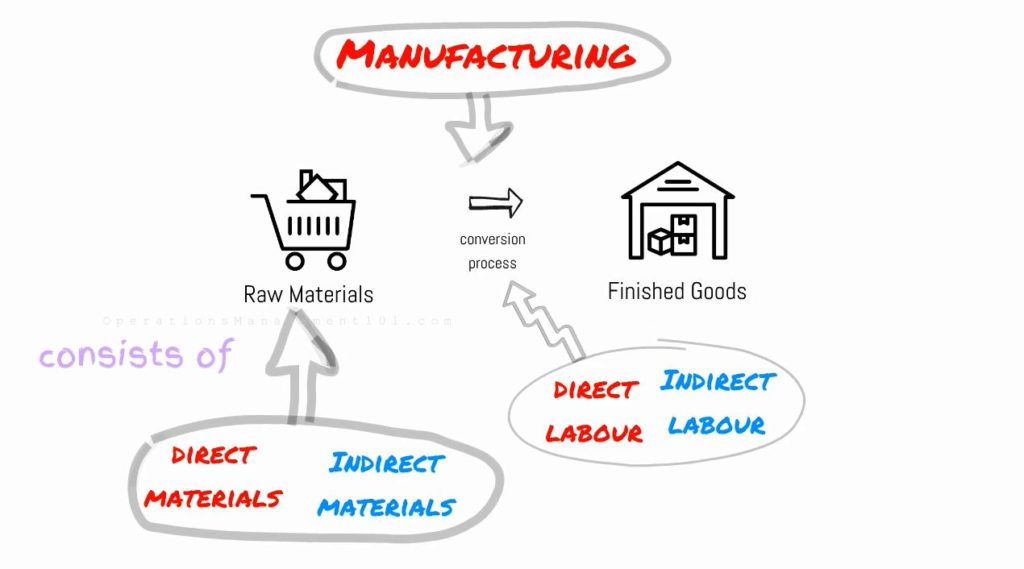
So, different types of costs in manufacturing can be generally classified into the following categories :
- Direct Materials costs
- Direct Labour costs
- Manufacturing Overhead (MOH)
Now we will see each of these one by one.
Direct Materials
Direct materials are raw materials which can be physically and directly associated with the finished product in the manufacturing process. Steel used in car production and flour used in bread production are some examples of direct materials.
Indirect Materials
Indirect materials are materials which do not become part of the finished product. Or they can not be linked to a specific product because their quantity is so small on a per product basis. Glue, lubricants etc. are examples of indirect materials.
Direct Labour
The work of employees which can be physically and directly associated with converting raw materials to finished products is called direct labour. Wages of bakers, bottlers, packers etc. are examples of direct labour.
Indirect Labour
Work of employees who support the production process; but who are not directly involved in converting raw materials to a physical product is called indirect labour. Wages of maintenance people, supervisors etc. are examples of indirect labour.
Manufacturing Overhead (MOH)
Manufacturing Overhead consists of costs that are indirectly associated with the manufacture of finished product.
Examples are indirect materials, indirect labour, depreciation of factory buildings and machines, tax, insurance etc.
All manufacturing costs that can not be classified as direct materials and direct labour comes under Manufacturing Overhead.
Manufacturing Overhead is also known as factory overhead or indirect manufacturing costs.
Other cost terms used in manufacturing accounting systems are following:
Total Manufacturing Costs
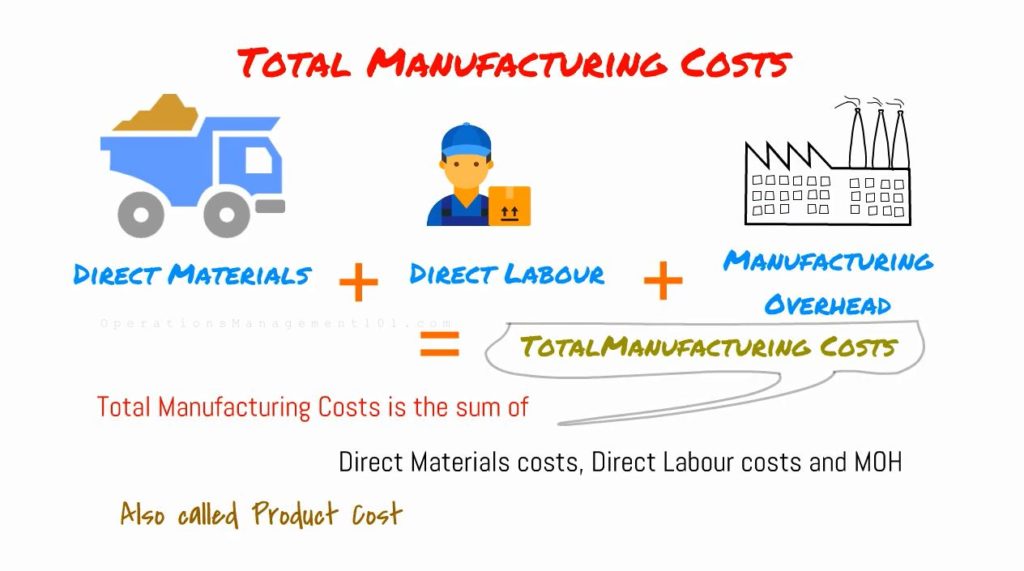
Total Manufacturing Costs is the sum of Direct Materials costs, Direct Labour costs and Manufacturing Overhead. Total Manufacturing Costs is also called Product costs.
Prime Costs and Conversion Costs
Another way of categorization is Prime costs and Conversion costs.
Prime costs
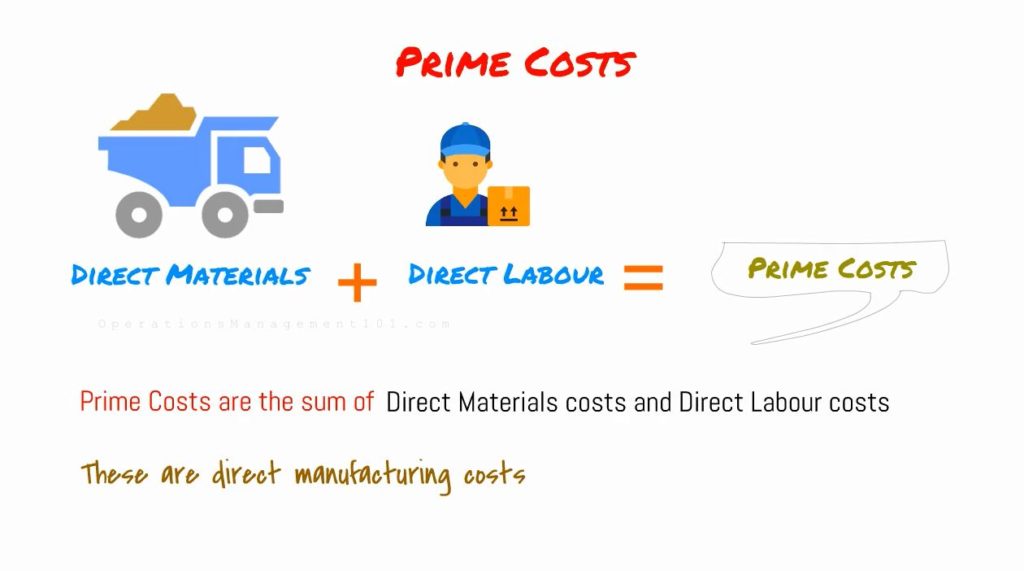
Prime costs are the sum of Direct Materials costs and Direct Labour costs. These are direct manufacturing costs.
Conversion costs
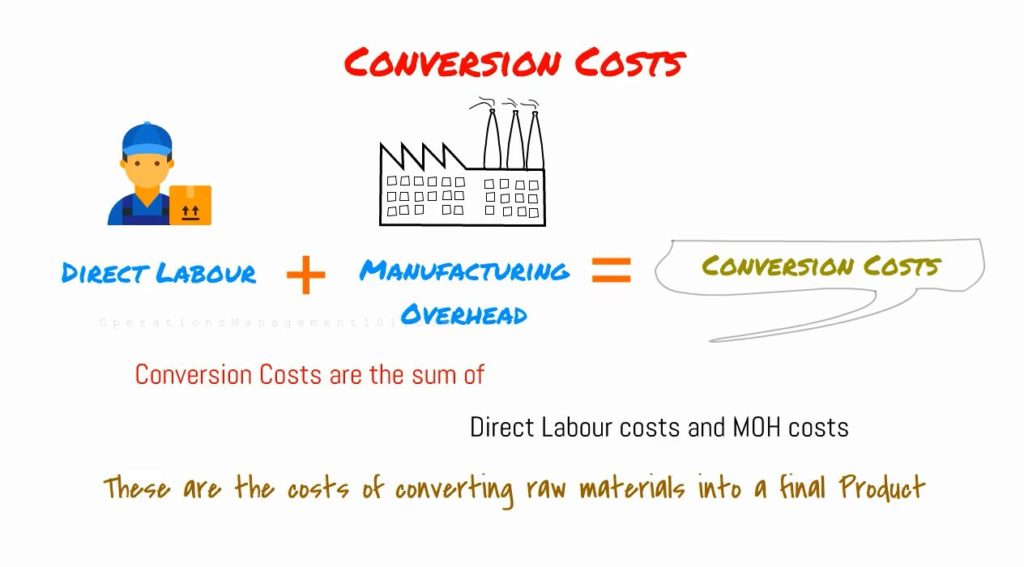
Conversion costs are the sum of Direct Labour costs and Manufacturing Overhead. These are the costs of converting raw materials to a finished product.
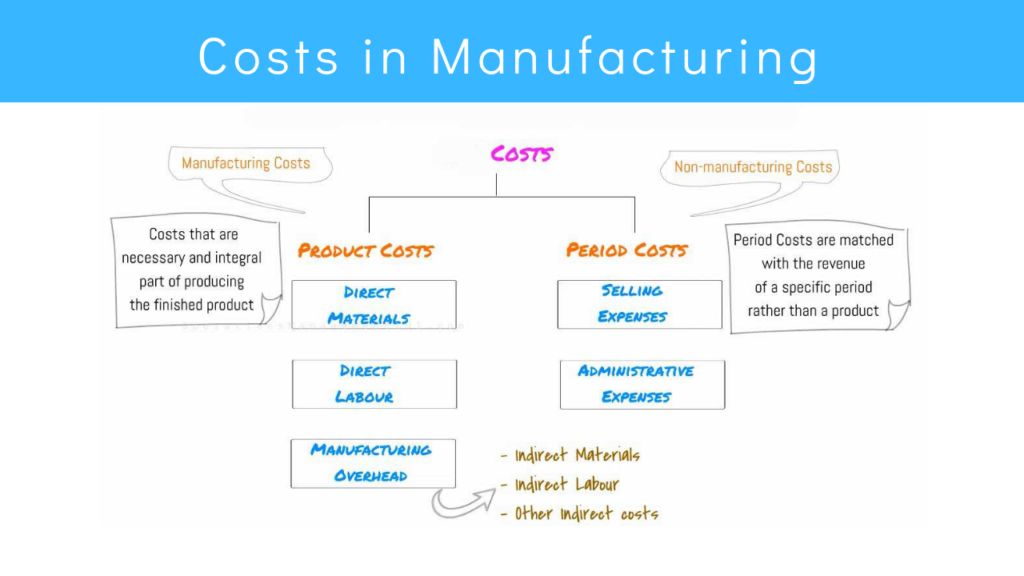
Product Costs and Period Costs
Product costs
Product costs consists of Direct Materials costs, Direct Labour costs and Manufacturing Overhead which are explained above in the section of Total Manufacturing Costs.
Period costs
Period costs are non-manufacturing costs. Period costs are matched with revenue of a specific period rather than a product.
Selling expenses and general administrative expenses are examples of period costs. They are deducted from revenue in that period to calculate net income.
In general, all costs involved in manufacturing can be classified into different categories and sub-categories as shown in the following diagram.